The report by The International Energy Agency highlights the current state of global natural gas markets, with a focus on supply, demand, and market trends. Despite record-breaking demand forecasts for 2024 and 2025, largely driven by Asia, the global gas balance remains fragile due to constrained LNG production and geopolitical tensions. A shift towards long-term, destination-fixed LNG contracts is observed, suggesting a return to more traditional features in the market. However, increased liquidity and diverse pricing mechanisms are expected in the medium term. The report also explores the role of low-emissions gases in the transport sector as a key driver of future demand.
Natural Gas Supply Security in 2024: Key Themes and Events
This briefing document reviews the main themes and significant events related to natural gas supply security in 2024, drawing on excerpts from the “Review of key gas supply security events in 2024.”
Executive Summary
While the global natural gas market has seen a degree of stabilisation in 2024 following the 2022-23 supply shock, it remains fundamentally tight. Below-average LNG supply growth and geopolitical uncertainties, particularly concerning Russian gas transit, contribute to this persistent volatility. This vulnerability is further highlighted by the increasing dependence on natural gas for electricity security, as demonstrated during extreme weather events across the globe. The disruption of key LNG shipping routes, including the Panama and Suez Canals, has increased logistical challenges, although the LNG carrier fleet has demonstrated some flexibility in adapting to these changes.
Key Themes
- Persistent Price Volatility: Despite some softening from 2022 highs, natural gas prices remain volatile due to tight supply fundamentals and geopolitical uncertainty.
“Historical monthly volatility on the TTF month-ahead contract averaged 50% in Q1-Q3 2024, standing 34% above the historical average during 2010-21.”
- Gas as Critical for Electricity Security: Natural gas plays a vital role in maintaining electricity supply security, particularly during extreme weather events that disrupt traditional generation sources like hydropower. The flexibility of gas supply, achieved through storage, LNG procurement, and pipeline interconnectivity, is crucial in these situations.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty Impacts Supply: The future of Russian gas transit through Ukraine poses a significant uncertainty for the 2024/25 winter season. With the expiration of existing transit agreements, some Central and Eastern European markets, particularly Moldova, face potential supply disruptions.
“The halt of this gas transit would translate into the loss of around 6 bcm of gas supply into the European Union in Q1 2025.”
- LNG Shipping Constraints Pose Challenges: While not leading to major disruptions, logistical challenges in 2024, such as low water levels in the Panama Canal and security concerns near the Suez Canal, highlight the vulnerability of LNG shipping routes. Despite these obstacles, the LNG carrier fleet has adapted by rerouting, leading to longer voyages and increased ton-mile demand.
Notable Events
- Winter Storm Wheather (United States): This event caused a surge in natural gas demand for heating, with gas-fired power generation meeting nearly 80% of the increased electricity demand. The event highlighted the critical role of gas storage in mitigating supply disruptions during extreme weather.
- El Niño Drought (Colombia): This prolonged drought significantly reduced hydropower output, leading to a surge in gas-fired power generation and increased reliance on LNG imports. The event underscored the importance of a diverse energy mix and robust import infrastructure.
- Prolonged Heatwave (India): This event led to record-high electricity demand for cooling, with gas-fired power generation reaching multi-year highs. The successful management of this demand surge demonstrated the benefits of increased LNG import capacity and domestic gas infrastructure development.
Looking Ahead
The briefing highlights the continued importance of ensuring natural gas supply security through a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Diversifying supply sources
- Investing in storage capacity and LNG infrastructure
- Enhancing energy efficiency measures
- Promoting regional cooperation to address potential supply disruptions
The uncertain geopolitical landscape and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events underscore the need for ongoing vigilance and proactive measures to ensure reliable and affordable natural gas supply in the years to come.
Global Gas Market Update: Q1-Q3 2024
This briefing document analyses recent trends in the global gas market, drawing upon data from the “Gas Market Update” report.
Key Highlights
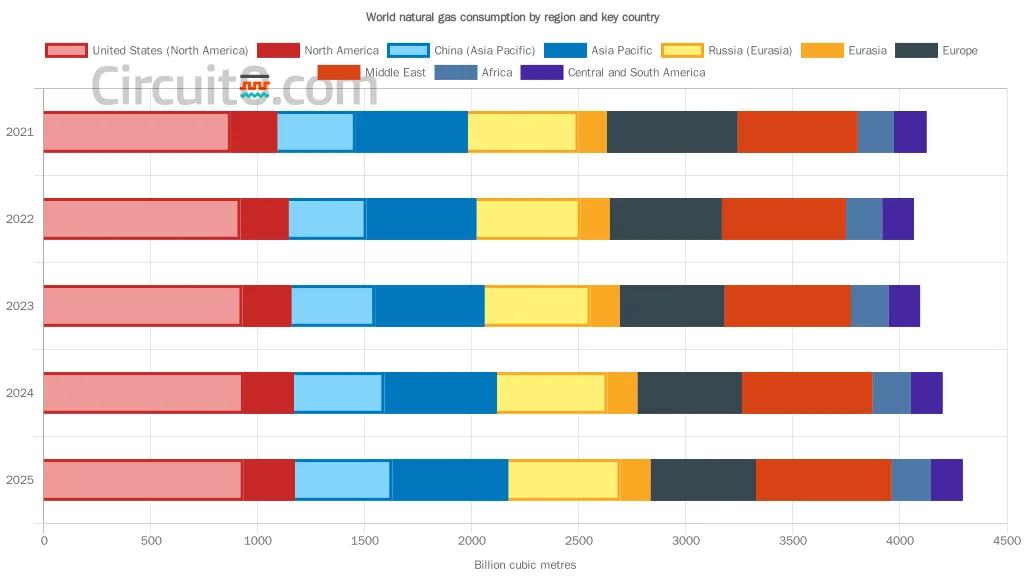
- Demand Growth: Global gas demand surged by 2.8% in Q1-Q3 2024, exceeding historical averages. This growth, fuelled by economic recovery and weather events, was primarily driven by Asia and the industrial sector.
- Supply Constraints: LNG supply growth remained limited, while geopolitical tensions, particularly surrounding Russia, impacted pipeline flows. This contributed to upward pressure on gas prices.
- Regional Variation: Demand patterns varied significantly across regions. While Asia experienced strong growth, European consumption declined due to energy efficiency measures and increased renewable energy generation.
- Price Volatility: Gas prices rose in key Asian and European markets due to tight supply-demand balances. However, abundant production kept US prices relatively low.
- Storage Dynamics: Despite slower injections, storage levels in Europe and the United States remain robust ahead of winter 2024/25.
Demand Drivers and Regional Trends
- Industry Leads Demand Growth: “Demand growth was largely supported by higher gas use in industry, contributing almost 60% of the demand growth in Q1-Q3 2024.” This trend is expected to continue, particularly in Asia.
- Asia’s Resurgence: Asian gas demand expanded by nearly 7% year-on-year, with China and India leading the way. “In 2024 Asian gas consumption is set to increase by more than 5%, with 70% of the growth coming from China alone.”
- European Declines: OECD Europe saw a 3% decline in gas consumption, driven by energy efficiency measures, renewables expansion, and a mild winter. “The power sector continued to be the most important driver behind lower gas use.”
- North American Resilience: North American gas demand rose by an estimated 1%, primarily driven by gas-to-power demand, particularly during heatwaves. However, milder weather moderated residential and commercial consumption.
Supply Challenges and Outlook
- LNG Supply Bottlenecks: “Limited LNG supply growth and geopolitical tensions provided upward pressure on gas prices across key import markets in Q2-Q3.” Project delays threaten to extend tight market conditions.
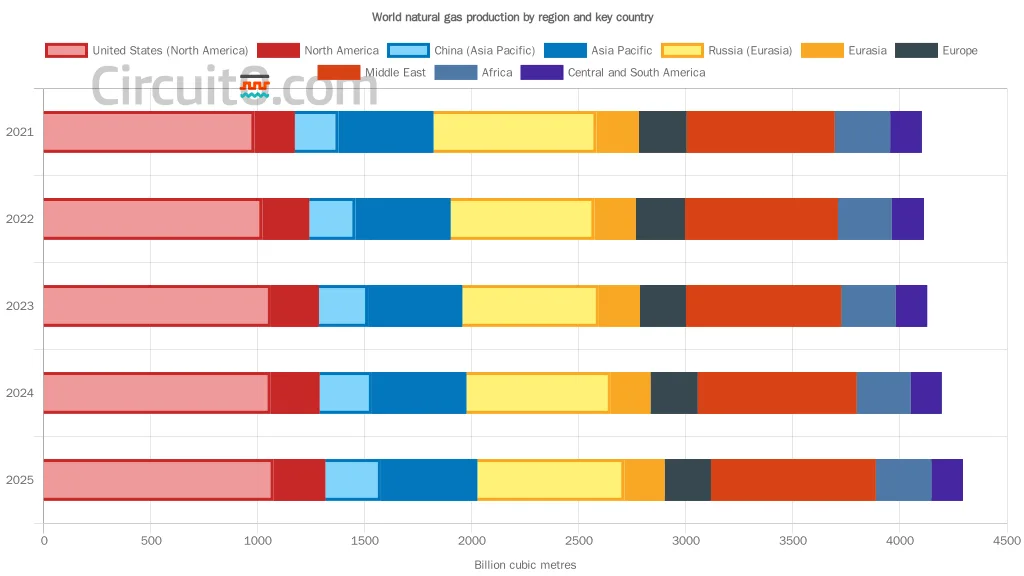
- US Production Rebalancing: US dry natural gas production experienced a slowdown in decline during Q3 due to price recovery. However, underlying trends point towards production recovery in 2025.
- Russian Supply Uncertainty: The expiry of the Russia-Ukraine transit agreement poses a significant risk to European gas supply in 2025. “This forecast assumes that Russia’s piped gas deliveries via Ukraine will halt at the beginning of 2025.”
- African Potential: Africa, with its vast gas reserves, is poised to enhance production and exports. “North Africa and West Africa are set to drive African natural gas and LNG exports respectively.”
Price Trends and Outlook
- Asian and European Price Increases: TTF and JKM prices rose in Q3 due to tight supply-demand balances. “The intensifying fighting on the Russia-Ukraine border – including near the Sudzha gas metering station – fuelled additional price volatility in August.”
- US Price Stability: Abundant production, particularly associated gas, has kept US prices low. “Record high associated gas production and the saturation of processing and pipeline takeaway capacity drove down Permian gas prices into negative territory.”
- Forward Curve Expectations: Forward curves suggest potential price increases in 2025, reflecting anticipated tighter market fundamentals. The price differential between Asian and European hubs is expected to tighten.
Implications and Considerations
- The global gas market remains finely balanced, with supply security concerns, particularly in Europe, persisting.
- Project delays and geopolitical tensions could exacerbate price volatility in the coming years.
- The surge in Asian demand, driven by economic growth, presents both opportunities and challenges for global gas suppliers.
- The energy transition plays a crucial role in shaping long-term gas demand, particularly in regions actively pursuing decarbonisation strategies.
Conclusion:
The global gas market is navigating a complex landscape of evolving demand patterns, supply constraints, and geopolitical uncertainties. While 2024 has witnessed some easing of market tightness, challenges remain, demanding careful monitoring and strategic planning to ensure a reliable and affordable gas supply in the years ahead.
LNG Market Update: Flexibility, Shifting Dynamics, and Future Trends
This briefing document analyses recent trends in the Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) market, drawing upon data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and industry reports.
Key Highlights
- Growing Flexibility: The LNG market is transitioning towards increased flexibility, characterized by a rising share of destination-free contracts and diverse pricing mechanisms.
- Shifting Geopolitics: The Middle East is emerging as a dominant player in LNG production and contracting, challenging North America’s recent dominance.
- Portfolio Players Prove Crucial: Portfolio players are playing an increasingly important role in ensuring market liquidity and bridging supply-demand gaps.
- Long-term Contracts Remain Relevant: Despite growing flexibility, long-term agreements continue to underpin market stability and provide security for both buyers and sellers.
Detailed Analysis
1. Evolution of LNG Contracting:
- Destination Flexibility: While destination-fixed contracts have seen a recent uptick, driven by Asian buyers, the overall trend points towards greater destination flexibility.
- “The share of destination-free contracts rose from 30% in 2016 to 47% in 2023… [and] is expected to increase to 51% by 2027.”
- Pricing Diversity: The reliance on oil-indexed contracts is declining, replaced by hub indexation and hybrid pricing models. This shift is expected to continue.
- “The share of oil-indexed LNG export contracts declining from over 70% in 2016 to 56% in 2023… [and] to shrink further to 52% by 2027.”
- Dominance of Long-term Agreements: Long-term contracts (10 years or more) represent the majority of contracts signed, reflecting a preference for security among buyers and sellers.
- “Long-term agreements (with a duration of 10 years and over) accounted for 85% of the volumes contracted since 2022.”
2. Regional Dynamics:
- Middle East’s Rise: Driven by Qatar’s ambitious expansion plans and projects in Oman and the UAE, the Middle East is poised to become a leading LNG supplier.
- “The Middle East emerged as the most important driver behind new LNG project approvals in 2024, led by Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Oman.”
- North America’s Shifting Role: Despite a recent slowdown in FID approvals, North America is expected to remain a significant player, with its LNG exports projected to increase substantially by 2027.
- “On the export side, the volume of supply contracts from North America is expected to increase by approximately 90% between 2023 and 2027.”
- Asian Buyers Drive Demand: Asian countries, particularly China and India, continue to be major importers of LNG, securing long-term contracts to meet growing energy demands.
- “Asian buyers continue to drive new LNG purchase contracts.”
3. The Rise of Portfolio Players:
- Bridging Flexibility and Security: Portfolio players are acquiring LNG from diverse sources through long-term contracts and reselling it through shorter-term or spot contracts, enhancing market liquidity.
- Growing Net Open Position: Portfolio players’ increasing net open position, the share of purchased LNG not committed to long-term sale contracts, further enhances market flexibility.
- “The growing net open position of portfolio players will contribute to market stabilisation by providing increased trading flexibility with regard to contract duration and volume.”
4. Future Outlook:
- Expanding LNG Capacity: With nearly 270 bcm/yr of new liquefaction capacity expected by 2030, the market is projected to experience increased supply.
- Evolving Market Dynamics: Expiring contracts, combined with new production capacity, will create opportunities for new contracts and potentially reshape long-term market dynamics.
- Destination Flexibility and Uncontracted Capacity: The increase in both destination-flexible contracts and uncontracted capacity is set to further enhance market liquidity and responsiveness to price fluctuations and geopolitical events.
Conclusion:
The LNG market is undergoing a period of significant transformation, characterized by a move towards greater flexibility, shifting regional dynamics, and the increasing influence of portfolio players. While long-term contracts will remain critical, the growing prominence of destination-free agreements and diverse pricing mechanisms is contributing to a more liquid and responsive global LNG market. This evolving landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for market participants as they navigate a future marked by evolving energy security priorities and potential price volatility.